Our Business Growth Tool Kit
As a team, our business growth experts all have a range of skills and experience to support you in overcoming the challenges you may be facing in your business, allowing you to unlock your true potential and that of your business. Throughout working with 1000s of business owners, our experts have developed and curated collection of the best tools & systems that they use with clients every single day.
Here’s what you’ll find in our Tool Kit:
3 “O” Model: This describes and models the 3 main types being Functional, divisional or product structures and helps you decide which structure works best for your organisation. Where we use this most: Organisational Structure

3 Circles Model: John Adair created the “3 Circles Model” to represent three core management responsibilities: 1. Achieving tasks 2. Managing the team or group 3. Managing individuals. Where we use this most: People Strategy
360 Degree Appraisal: unlike a traditional appraisal, a 360-degree appraisal gathers information from a number of sources such as colleague opinions, customer opinions and direct reports to give a more holistic review of performance. Where we use this most: People Strategy, Employee Engagement, Succession Planning
5-3-1 Vision Orbit: This planning model allows you to look out 5, 3 and 1 year across all aspects of the business ensuring there is a road map that makes sense and brings visibility to the business. Where we use this most: Business Planning
Accounts Receivable Analysis: the monies owed to a business by its customers are called “Accounts Receivable” and an analysis of these accounts can indicate the health of a company’s cash flow/ working capital. Where we used this most: Improving Working Capital
Activity-Based Costing (ABC): this is an accounting method used to determine the total cost of activities needed to deliver a service or make a product whereby costs are assigned specifically to each activity. Where we use this most: Increasing Profits
Aptitude Testing: in order to understand how a candidate learns, what their reasoning skills are and their general ability to perform workplace tasks, aptitude testing can be a valuable tool. Where we use this most: Recruiting for Success
Balanced Scorecard: A balanced scorecard is a tool used by managers for measuring strategy performance. It allows managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences or risks. Where we use this most: Improving Productivity, Creating High Performing Teams
Blue Ocean Strategy Planning: a strategic planning model that removes focus from competitive and overcrowded markets, and instead focuses on identifying new markets and innovation. Where we use this most: Strategic Planning
Budgeting: in its most simplistic form, a budget is a financial plan for the future which gives an organisation financial control around income, expenditure and targets. Where we use this most: Financial Planning
Career Anchors: a concept created by Edgar Shein, career anchors describe a person’s perception of their own values, talents, abilities and motives. By understanding how the individual perceives themselves, we are able to nurture them to be their best whilst also challenging them to grow and develop. Where we use this most: Developing Talent
Career Strategy Planning: looking at the skills of the team and future requirements you can plan out where you will need resource and if that will come from within the organisation or need to be recruited for. Where we use this most: Developing Talent

Cash Gap Analysis: analysis of a cash gap can demonstrate how cash “flows” through an organisation and identify both any risks where the gap is too large and opportunities to reduce the gap. Where we use this most: Improving Working Capital
Cashflow Forecasting: an estimation of an organisation’s future financial position, and it allows the organisation to prepare the necessary cash it needs to meet fulfil obligations whilst avoiding any funding issues. Where we use this most: Financial Planning
Competency Framework Analysis: A competency framework is a means by which organisations communicate which behaviours are required, valued, recognised and rewarded with respect to specific roles. Where we use this most: Building Competencies
Core Competencies Analysis: identifying the strengths of a business that differentiate it from its competitors and how well theses strengths are capitalised for their advantage. Where we use this most: Creating the Vision
Cost Base Analysis: Cost-benefit analysis is a systematic approach to estimating the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives used to determine options which provide the best approach to achieving benefits while preserving savings. Where we use this most: Increasing Profits
DiSC Behavioural Analysis: a DiSC Assessment identifies personality traits and behaviours of a person and scores them in 4 different categories (Dominance, Influence, Steadiness & Conscientiousness) allowing teams to understand one another in more depth and communicate more effectively. Where we use this most: Creating the Vision
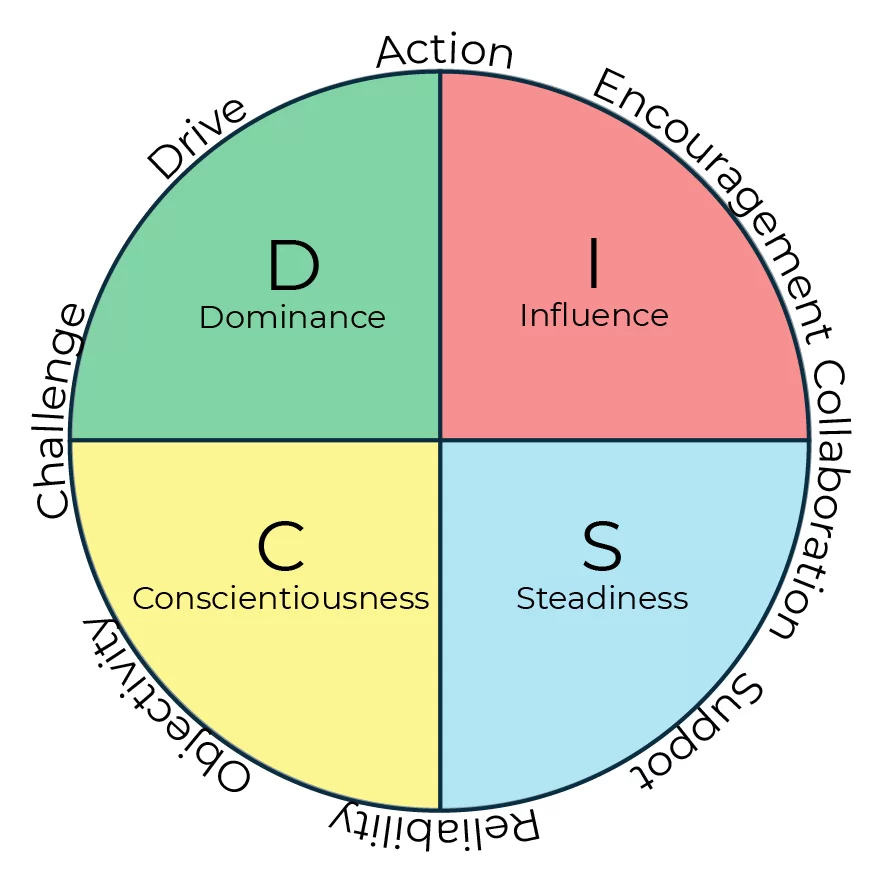
DiSC Leadership Analysis: DISC profiles help us identify a leader’s preferred behavioural style; think of it as a road map showing how a leader is likely to show up in different situations. We can predict how they tend to do things, such as lead others, make decisions, and communicate Where we use this most: People Challenges
Employee Engagement Analysis: employee engagement is measured from a holistic perspective to understand how invested employees are in a business & its goals, which in turn determines how motivated they are to deliver on their individual responsibilities and how likely they are to remain with the company. Where we use this most: Operational Effectiveness
Engagement Multiplier: employee engagement software that is built to improve your organisation’s productivity and increase ROI. Where we use this most: Employee Engagement
Executive Coaching: Executive coaching is a form of organisational learning through one-to-one conversations that facilitates development for a leader. It can be used in a variety of ways, for example, getting past an impasse, removing a stumbling block or drawing out and building on strengths. Where we use this most: Developing Talent
Book A Call
Why not get in touch with the team today? We’d love to hear from you!
We’re truly passionate about supporting business owners like you overcome your challenges and unlock the true potential of your business. If you’re looking to drive your business forward, get in touch today!
Gap Analysis: a Gap Analysis is a method of evaluating a business’ performance against different objectives to determine whether they are being met or not, and if not, what needs to be done to ensure they are met. Where we use this most: Risk Management
Growth Score Cards: The balanced scorecard greatly improves traditional financial reporting because it focuses on three things which lead to growth: customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and future growth opportunities. Where we use this most: Scaling Up
Inventory Analysis: understanding the “optimum” level of inventory for a firm is essential to remove the risk of holding onto the redundant or slow-moving stock, whilst optimising the opportunities to fulfil high-demand orders. Where we use this most: Improving Working Capital
Leadership vs Management Matrix: This matrix looks at the key skills and attributes required for each role and responsibility and how each influence the businesses success. Where we use this most: Creating High Performing Teams
LION Meetings: LION is a meeting structure designed to allow teams, senior managers and business owners have more purposeful and effective meetings. The meeting is broken down into 4 segments (Last Week, Issues, Opportunities, Next Week) to keep people focused on the purpose. Where we use this most: Management Skills
Management by Value-Based Objectives: Value-Based Management (VBM) is the management philosophy and approach that enables and supports maximum value creation in organisations, typically the maximization of shareholder value. VBM encompasses the processes for creating, managing, and measuring value. Where we use this most: Exit Planning
Margin Analysis: margin analysis allows us to identify not just that we are making profit but what product or service is making us the margin between cost and revenue. Its often hidden away in the average gross margin but splitting it down is where the true improvement comes from. Where we use this most: Organisational Efficiencies

McKinsey 7s Model: the 7s Framework is a tool to analyse a business’ organisational design against 7 categories: Structure, Strategy, Systems, Skills, Style, Staff and Shared Values. Where we use this most: Scaling Up
McKinsey 7 Degrees of Freedom Model: this model was created by partners at McKinsey to address constraints leaders “subconsciously apply” when planning to grow their business. Where we use this most: Growth Funding
Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS is a customer loyalty indicator calculated by asking customers how likely they are to recommend a product or service to a friend or colleague on a scale of one to ten. Here’s a great blog all about the importance of measuring NPS. Where we use this most: Building Asset Value
Organisational Competency Gap Analysis: A skill gap analysis helps to identify the skill gaps an individual or group of individuals has. Conducting a skill gap analysis is a three-step process that includes determining desired skills, assessing a candidate’s skills and identifying gaps. Where we use this most: Building Competencies
Organisational Design Analysis: Organisational analysis focuses on the structure and design of the organisation and how the organisation’s systems, capacity and functionality influence outputs. Additional internal and external factors are also accounted for in assessing how to improve efficiency. Where we use this most: Organisational Structure
Organisational Efficiency & Control Modelling: Organisational effectiveness can be defined as the efficiency with which an association is able to meet its objectives. … If the organisation has both organisational effectiveness and efficiency, it will achieve its goal of making a profit by producing and selling a product without waste. Where we use this most: Organisational Efficiencies
Organisational KPIs: are the critical (key) indicators of progress toward an intended result. Leading indicators are precursors of future success; lagging indicators show how successful the organisation was at achieving results in the past. Where we use this most: Performance Management
Organisational Skills Gap Analysis: This skills gap analysis looks wider than a team or an individual and looks to the wider organisation and the skills required to deliver its operational and strategic goals. Where we use this most: Succession Planning
Performance Appraisals: A performance appraisal is a regular review of an employee’s job performance and overall contribution to a company. Also known as an annual review, performance review or evaluation, or employee appraisal, a performance appraisal evaluates an employee’s skills, achievements, and growth or lack thereof. Where we use this most: Performance Management
Porter’s 5 forces: this tool was created to highlight alternative variables that impact the profitability of an industry. The 5 variables are; Competitive Rivalry, Supplier Power, Buyer Power, Threat of Substitution and Threat of New Entry. Where we use this most: Increasing Profits

Porter’s Diamond: Porter’s Diamond model demonstrates which factors impact a nation’s competitive advantage over another. This allows businesses to research and understand new markets ahead of investing in them to ensure the opportunity is viable. Where we use this most: Strategic Planning
Positional Contracts: unlike a traditional contract, a positional contract is an agreement that explicitly states who the employee reports to, and the output and results expected from their work. Where we use this most: Management Skills
Psychometric Testing: a psychometric test is a tool that employers can use to assess a candidate’s suitability more holistically. This allows the employer to evaluate skills, knowledge, abilities, personality traits, attitudes and potential. Where we use this most: Recruiting for Success
Remote Leadership Model: The ability to lead a team, remotely and in a virtual world without the normal cues that come from face to face leadership. Where we use this most: Organisational Structure
Return On Capital Invested Modelling: In other words, it is the expected compound annual rate of return that will be earned on a project or investment. IRR is usually compared to a company’s WACC to determine whether an investment is worthy or not. Where we use this most: Growth Funding
Revenue Analysis: by analysing revenues over a time period, a business can determine if their revenue is growing, which products/services are their main revenue drivers, individual product revenues and more. Where we use this most: Building Asset Value
Risk Impact / Probability Modelling: Impact and probability are the two main components of Risk analysis. … In risk analysis, the risk is traditionally defined as a function of probability and impact. The probability is the likelihood of an event occurring and the consequences, to which extent the project is affected by an event, are the impacts of risk Where we use this most: Managing Risk
Scenario Planning: identifying potential risks and uncertainties to make flexible long-term plans, based on alternative outcomes. Where we use this most: Succession Planning
Have you tried our Milestone Survey?
Understand what stage your business is currently at, and get a bespoke report that will help you take it to the next level!
Setting The Bar Analysis: This tool focusses on the core competencies required to hit specific targets and goals across the organisation. Where we use this most: Building Competencies
Situational Leadership: a framework introduced by Hersey & Blanchard, situational leadership takes into account both the leadership style but also the developmental stage of the employee. It consists of 4 areas: Telling, Selling, Participating and Delegating. Where we use this most: Creating High Performing Teams
Skill:Value Matrix: this matrix helps to evaluate tasks based upon the value the task provides for the company, and what level of skill is needed to complete the task. This helps business owners and their teams manage tasks in the most effective way, decide on outsourcing, and ensure the time invested is delivering a return. Where we use this most: Improving Productivity
Soft Systems Methodology: Soft systems methodology is an approach to organisational process modelling and it can be used both for general problem solving and in the management of change. Where we use this most: Managing Risk
Step Ladder Technique: a method to deliver effective decision making within a team, whilst ensuring contributions from all team members are acknowledged and considered whilst the decision is made. The method has 5 steps: Identifying the problem, Building the ladder, Continuing the process, Complete the ladder and Making a decision. Where we use this most: Employee Engagement
Success Profiling: a success profile is created during the succession planning process in order to clarify the criteria and requirements of a role both right now and the future of the role. Where we use this most: Recruiting for Success
Supply Chain Analysis: This tool ensures there is a review of the whole supply chain and looks to reduce or eliminate risk, introduce cost-saving or innovation and ensure future growth potential can be delivered through existing suppliers. Where we use this most: Building Asset Value

SWOT Analysis: used for the evaluation of both an individual or a business, a SWOT analysis is used to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats to ensure risks are managed and advantages are optimised. Where we use this most: Business planning
TDODAR Decision Model: used in high-pressure situations for decision making, TDODAR (Time, Diagnose, Options, Decide, Assign, Review) is a decision-making framework to ensure that all elements of a decision are reviewed to create the best outcome. Where we use this most: Business Planning
Team Member KPIs: A measure of activity or performance of an individual to ensure each team member has accountability within the organisation and is aligned to the wider goal. Where we use this most: Performance Management

The Golden Circle: developed by Simon Sinek, the Golden Circle is a concept that describes how a business presents a solution to a problem. The focus is removed from “what” the company delivers and focuses in on “why” the company does it. Where we use this most: Shared Values & Culture
Three C’s Model: Ohmae’s Three C’s Model centres around: the Customer, Competitors and the Corporation. Ohmae suggests that these three C’s are essential for success when planning a strategy. Where we use this most: Scaling Up
Time Management Matrix: Stephen Covey’s Time Management Matrix is a tool that supports prioritising activities based on urgency and importance. Where we use this most: Improving Productivity
True Colours: This personality test allows individuals to be categorised but 4 main colour types, orange, gold, green and blue to help aid team-building and self-awareness. Where we use this most: Management Skills
USP Analysis: analysis of a product or service to determine the unique/special features that are marketed to the target audience and distinguishes the product or service from its competitors. Where we use this most: Management Skills
Value Builder: The Value Builder System™ is a tool that scores a business against 8 key drivers of business value. The tool identifies opportunities to increase the value of a business and reduces the risk of a low sale price. Where we use this most: Exit Planning
Value Chain Analysis: this process involves a business reviewing the activities involved in creating a product or delivering a service. This analysis allows progress to be made towards creating competitive advantage, improve efficiency and increase profit margins. Where we use this most: Strategic Planning, Exit Planning, Operational Effectiveness
Value Disciplines Model: a framework created by Treacy and Wiersema, the Value Disciplines model proposes that for a business to be competitive they must perform well in three key areas: Customer Intimacy, Product Leadership and Operational Excellence. Where we use this most: Shared Values & Culture

VMOST Analysis: the VMOST Analysis is an evaluation of a business’s core strategies to ensure that the supporting activities of a strategy are being carried out. The focus of a VMOST Analysis is on 5 core elements: vision, mission, objectives, strategies and tactics. Where we use this most: Operational Effectiveness
Working Capital Analysis: used to determine the liquidity of a business’s current assets in comparison to its current liabilities. Where we use this most: Growth Funding
